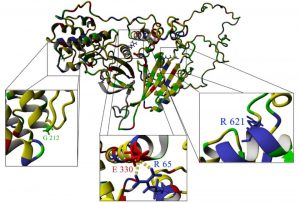
The BRSK2 gene encodes an enzyme that aids in the growth of axons in neurons. By analyzing the DNA of 371 children with unexplained delay or disability, the researchers were able to identify genetic causes through sequencing. The addition of five more individuals with BRSK2 mutations brought the total to nine. Whole-genome sequencing, which was previously not feasible, was used in this study, which may explain why the BRSK2 gene had not been linked to neurodevelopmental conditions before.
While researchers are uncertain if BRSK2 is exclusively an autism gene, the discovery offers families affected by BRSK2 mutations a more precise diagnosis. The identification of a BRSK2 mutation provides tangible benefits for affected families, such as connecting with others facing similar experiences through personal and social media interactions. Additionally, pinpointing mutations related to brain conditions may have future therapeutic implications.
